Blog
Types of Pumps and Tips for Selecting the Right One?
Choosing the right pump can be challenging. Understanding the various types of pumps is essential for making informed decisions. According to John Smith, an expert in the pump industry, "Selecting the right pump type defines your project's success."
There are several types of pumps available on the market. Each type serves a specific purpose, from centrifugal pumps to positive displacement models. Knowing their differences is crucial. For instance, centrifugal pumps work best for low-viscosity liquids, while positive displacement pumps excel in handling thicker substances.
It's important to consider specific project needs over general preferences. Overlooking details like flow rate and pressure can lead to costly mistakes. Remember, selecting from the many types of pumps requires careful thought. Balancing efficiency with cost-effectiveness is not always straightforward. The right choice can lead to better outcomes, while a wrong selection may cause complications.
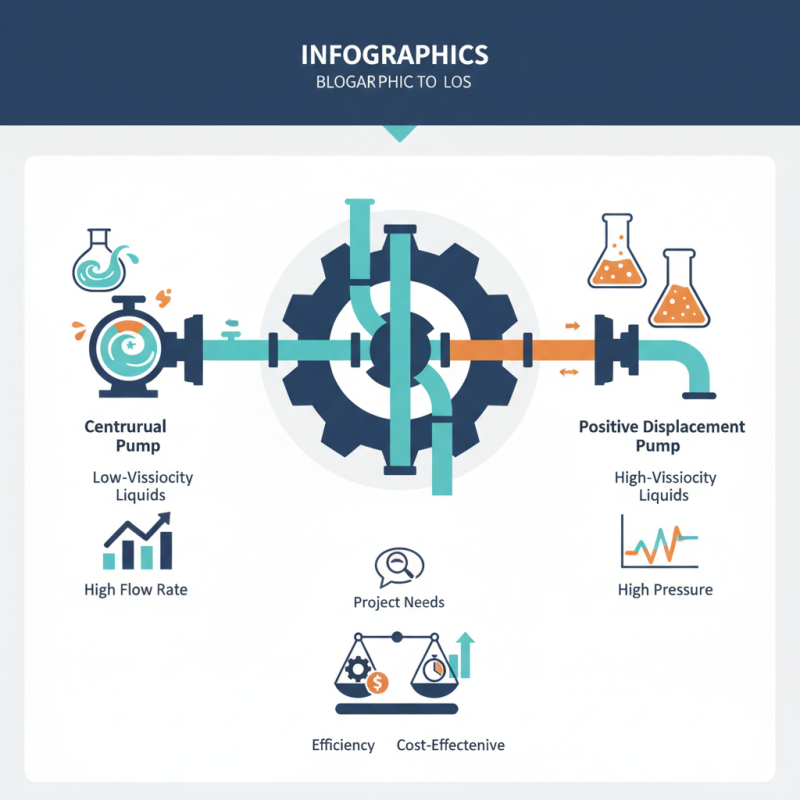
Types of Pumps: An Overview of Different Pump Categories
Pumps play a crucial role in various industries, ensuring the efficient transfer of fluids. Different types of pumps exist, each designed for specific applications. Centrifugal pumps, for instance, focus on moving large volumes of liquids at a relatively low pressure. According to a 2022 market analysis, these pumps account for about 75% of total pump sales globally, thanks to their efficiency and simplicity.
Positive displacement pumps, on the other hand, are crucial when dealing with highly viscous fluids. They operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge. Industry reports indicate that this type constitutes roughly 15% of the market but remains essential for oil, paint, and food industries.
Selecting the right pump can be challenging. Many overlook key factors like fluid viscosity and temperature tolerance. A surprising 30% of pump failures are attributed to improper selection, leading to costly downtime. It's vital to consider operational demands and fluid properties when making choices. Ignoring these factors can lead to inefficiencies and increased maintenance costs. Proper research and understanding of pump categories can greatly enhance decision-making.
Types of Pumps and Tips for Selecting the Right One
| Pump Type | Description | Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pump | Uses rotational energy to move fluids | Water supply systems, industrial processes | High flow rates, simple design |
| Positive Displacement Pump | Moves fluid by trapping a fixed amount and forcing it through the discharge | Chemical processing, food industry | Handles viscous fluids, precise dosing |
| Diaphragm Pump | Uses a diaphragm to create a variable volume chamber | Wastewater treatment, pharmaceuticals | Self-priming, great for shear-sensitive liquids |
| Submersible Pump | Designed to be submerged in fluid | Dewatering, groundwater extraction | Efficient in deep water, compact design |
| Gear Pump | Uses gears to pump fluid by displacement | Hydraulic systems, fuel pumping | High pressure, good for dense liquids |
Understanding the Functionality of Various Pump Mechanisms
Understanding the functionality of various pump mechanisms is crucial for selecting the right pump. Different types of pumps serve specific needs. Centrifugal pumps, for example, move fluid through rotational energy. They are efficient for high-flow applications. In contrast, positive displacement pumps are ideal for thicker fluids. They rely on trapping fluid and forcing it through the discharge. According to industry reports, centrifugal pumps account for about 80% of all pumps used globally.
Choosing the right pump depends on several factors. Flow rate, fluid viscosity, and system pressure are vital for proper selection. For instance, if you require high viscosity handling, screw pumps might be worth considering. They offer great performance but can be more complex to maintain. Additionally, pumps require a power source. Some may run on electricity, while others use hydraulics or air. This can add complications if not planned carefully.
Unexpected challenges often arise with pump selection. Sometimes, the required flow rates are not met. This can lead to inefficiencies. Users should regularly revisit performance data. A pump may perform well initially but fail under changing conditions. Regular monitoring and adjustments can help mitigate these issues. Familiarizing oneself with the intricacies of pump mechanisms can pave the path toward smarter decisions.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Pump
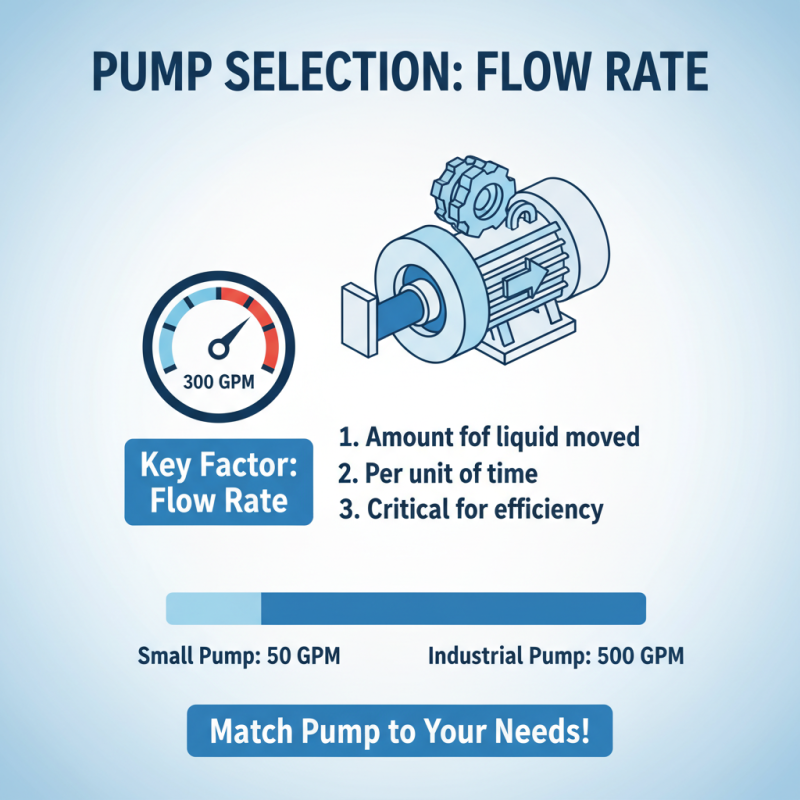
When selecting a pump, several key factors come into play. First, consider the flow rate. This measurement determines how much liquid the pump can move in a given period. For instance, many industrial pumps have flow rates ranging from 50 to 500 gallons per minute. Understanding your specific requirements is crucial for efficiency.
Another important factor is the pump's total head. This refers to the height to which a pump can raise water. A pump with inadequate head may lead to inefficient operations. Data suggests that a mismatch can lead to up to 30% more energy consumption, which could noticeably increase operating costs.
Here are some tips for selecting the right pump:
- Assess the viscosity of the fluid. Thicker fluids may require more powerful pumps.
- Check the suction lift. Some pumps may struggle with high suction lift requirements.
- Evaluate your system for maintenance needs. A pump requiring frequent maintenance can become a burden.
It’s important to also think about the environment where the pump will be used. Factors such as temperature and pressure can impact pump performance. However, many overlook these aspects, which may lead to costly errors down the line. A knowledgeable choice can prevent disruptions. Always consider consulting with a professional who understands the specific application.
Common Applications for Each Type of Pump
Pumps are vital in various industries. Each type serves unique functions and applications. Selecting the right pump can be challenging. Understanding their common uses helps.
Centrifugal pumps are widely used. They are perfect for moving liquids quickly. Many times, they find applications in water supply or chemical processing. They offer great flow rates. However, they may struggle with thick liquids. Assess the fluid's viscosity before choosing this type.
Positive displacement pumps provide another option. They work for thicker fluids. These pumps excel in applications needing precise dosing. For instance, they are crucial in food and beverage processing. However, they may not be as efficient for low-viscosity liquids. It’s important to match the pump type to the intended application carefully.
When selecting a pump, consider these tips. First, know the fluid characteristics. Identify viscosity, temperature, and chemical compatibility. Next, determine the required flow rate. Understand the system's overall pressure needs. Finally, think about maintenance needs. Some pumps require more frequent upkeep than others. Balancing these factors is essential for optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips to Ensure Optimal Pump Performance
Proper maintenance is crucial for pump performance. Regular checks can prevent costly failures. Research shows that 70% of pump issues are linked to inadequate maintenance. Neglecting routine tasks can lead to significant downtime.
To ensure optimal performance, keep pumps clean and lubricated. Contaminants can increase wear and tear. Operators should monitor pressure levels and vibrations regularly. Unusual noises might indicate a problem. Replace worn parts promptly. A small issue can escalate quickly if ignored.
Documentation is essential for effective maintenance. Record all service activities. This helps identify patterns in pump behavior. An analysis of past performance can guide future maintenance decisions. Balancing preventive measures with timely repairs is key to longevity.
Types of Pumps and Their Performance Ratings
This chart illustrates the flow rates of different types of pumps measured in liters per minute (L/min). When selecting a pump, it is important to consider the application, required flow rate, and the specific characteristics of each pump type to ensure optimal performance.
Related Posts
-

How to Optimize Pump Technology for Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs
-

How to Choose the Right Commercial Pump for Your Business Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Pump Systems for Your Specific Needs
-
Understanding the Mechanics of Diaphragm Pumps: The Key to Efficient Fluid Transfer
-

2025 Top Chemical Metering Pump System Insights and Innovations
-

2025 Top 5 Chemical Metering Solutions for Precision and Efficiency
