Blog
What is an Industrial Pump? Understanding Types, Uses, and Benefits
Industrial pumps are vital components in various sectors, playing a crucial role in the transportation of fluids ranging from water to highly viscous materials. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in fluid dynamics and industrial pump technology, "Understanding the types and applications of industrial pumps is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs." This sentiment emphasizes the importance of comprehending the diverse landscape of industrial pumps, as their applications span numerous industries including manufacturing, mining, and agriculture.
Industrial pumps not only vary in design and function but also offer distinct benefits that can enhance productivity. By delving into the various types of industrial pumps, we can identify which specific models are best suited for particular tasks, whether it be centrifugal pumps for high-flow applications or positive displacement pumps for precise flow rates. Additionally, understanding the operational requirements and maintenance needs of these pumps is crucial for ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
In exploring the world of industrial pumps, we gain insights into their practical uses and the advantages they bring to modern industrial operations. From increasing efficiency to reducing downtime, the role of industrial pumps cannot be overstated, making it imperative for professionals in the field to stay informed about the latest developments and technologies in pump engineering.

Definition of Industrial Pumps and Their Functionality
Industrial pumps are essential mechanical devices designed to move fluids—liquids or gases—through various systems. Their primary function is to transport these fluids from one place to another, enabling processes across numerous industries, such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and water treatment. By creating a pressure differential or suction, these pumps facilitate the movement of materials, allowing for efficient operation in industrial settings.
There are numerous types of industrial pumps, each tailored to specific applications and fluid characteristics. Centrifugal pumps, for example, use a rotating impeller to impart kinetic energy to liquids, making them ideal for high-flow applications. Positive displacement pumps, on the other hand, trap a fixed amount of fluid and force it through the pump’s outlet, which is particularly useful for viscous fluids or when precise dosing is required. Understanding the functionality of these pumps not only helps in selecting the right type for particular tasks but also highlights their role in enhancing productivity and reliability within industrial processes.
What is an Industrial Pump? Understanding Types, Uses, and Benefits
| Pump Type | Uses | Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pump | Liquid transfer, refrigeration, and HVAC systems | High flow rates, simple design, and cost-effective | Water supply, irrigation, and cooling systems |
| Positive Displacement Pump | Viscous fluid transfer, and chemical dosing | Handles thick liquids and provides constant flow | Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals |
| Submersible Pump | Drainage and sewage systems | Efficient in deep well applications and low maintenance | Flood control, wastewater treatment |
| Diaphragm Pump | Chemical handling and food processing | Leak-free operation and ability to pump slurries | Mining, coatings, and agriculture |
| Gear Pump | Lubrication and fuel handling | Consistent flow at high pressures | Automotive, oil and gas |
Key Types of Industrial Pumps and Their Applications
Industrial pumps are essential components in various sectors, including manufacturing, chemical processing, and water treatment. Understanding the key types of industrial pumps and their applications can significantly enhance operational efficiency. The most common types include centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, gear pumps, and diaphragm pumps. According to a recent market analysis by Research and Markets, the global industrial pump market is projected to reach $80 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand in industrial applications.
Centrifugal pumps are widely used for liquids that are low in viscosity, making them ideal for water supply and chemical transfer. In contrast, positive displacement pumps are perfect for thick liquids and slurries, as they operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and displacing it to the discharge, which is critical in sectors such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. Gear pumps, recognized for their precise flow control, find applications in hydraulic systems and fuel handling, while diaphragm pumps are preferred in industries requiring leak-free operation, especially in hazardous material handling.
Tips: When selecting an industrial pump, consider the fluid's viscosity, temperature, and corrosiveness. Additionally, evaluate the required flow rate and pressure to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help extend pump lifespan and improve efficiency. Analyzing operational needs and potential environmental impacts is vital before making a choice, ensuring that the right pump is selected for the specific application.
Understanding the Components of an Industrial Pump
Industrial pumps are critical components in various sectors, facilitating the movement of liquids and slurries through a range of applications. Understanding the components of an industrial pump is essential for recognizing its functionality and maintenance needs. An industrial pump primarily consists of several key parts: the motor, impeller, casing, and seals.
The motor serves as the driving force of the pump, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to initiate fluid movement. Attached to the motor is the impeller, a rotating part that imparts kinetic energy to the fluid, causing it to flow. The casing surrounds the impeller, providing a controlled pathway for the fluid, while the design of the casing affects the pump's efficiency and performance. Seals play a crucial role in preventing leaks and maintaining pressure within the pump, essential for optimal operation.
Together, these components work harmoniously to ensure the effective transfer of fluids in various industrial processes. The design and material of each component can vary significantly depending on the specific application, influencing factors such as durability, resistance to corrosive substances, and temperature tolerance. Understanding these components allows for better selection and maintenance of industrial pumps, contributing to increased operational efficiency and longevity.
Industrial Pump Types and Their Applications
Benefits of Using Industrial Pumps in Various Industries

Industrial pumps play a crucial role in various sectors by efficiently moving fluids, slurries, and gases. One of the primary benefits of using industrial pumps is their ability to enhance operational efficiency. In industries such as manufacturing, water treatment, and oil and gas, these pumps ensure that materials are transported quickly and accurately, which minimizes downtime and maximizes productivity. By optimizing fluid movement, companies can streamline their processes, reduce labor costs, and improve overall performance.
Another significant advantage of industrial pumps is their versatility. They are designed to handle a wide range of fluids, from water and chemicals to heavy oils and slurries, making them indispensable in numerous applications. For instance, in the food and beverage industry, pumps are essential for ensuring hygiene while moving ingredients, while in construction, they facilitate the transfer of concrete mixtures. Additionally, many modern pumps come equipped with advanced technology, allowing for better control and monitoring of fluid dynamics, which further enhances safety and operational effectiveness across various applications.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Industrial Pumps
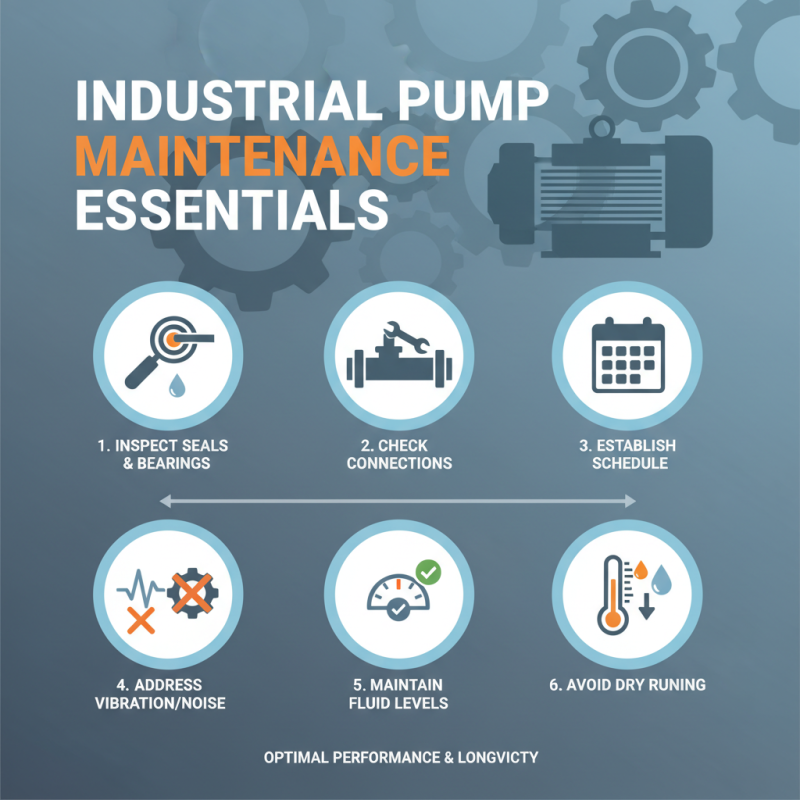
Maintaining industrial pumps is crucial for ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance checks should include inspecting seals, bearings, and connections to prevent leaks and mechanical failures. A maintenance schedule should be established based on the pump's operational environment and usage patterns. Addressing issues such as vibration irregularities or unusual noises promptly can prevent more severe damage. Maintaining correct fluid levels and ensuring the pump is not running dry are also essential to avoid overheating and extensive wear on internal components.
Troubleshooting industrial pumps involves identifying and resolving common problems that arise during operation. When encountering low flow rates, it’s important to check for blockages in the intake or discharge lines, as well as verifying that the pump is primed correctly. For pumps experiencing excessive noise, examining the alignment and securing of motor mounts may reveal underlying issues. Additionally, monitoring pressure levels can help detect incipient failures early, allowing for necessary adjustments or repairs. Implementing a systematic approach to troubleshooting can significantly reduce downtime and improve the overall efficiency of pumping operations.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Types of Pumps for Your Industrial Needs: A Comprehensive Guide
-

How to Choose the Right Commercial Pump for Your Business Needs
-

Understanding the Role of Industrial Metering Pumps in Modern Manufacturing Processes
-

How to Choose the Right Commercial Pump for Your Business Needs
-

2025 Top Chemical Metering Pump System Insights and Innovations
-

Top 10 Chemical Metering Solutions for Accurate and Efficient Measurement
