Blog
What is a Chemical Pump and How Does it Work?
Chemical pumps are essential in many industries, including chemical manufacturing, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global chemical pump market is projected to reach $5.36 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the increasing demand for efficient fluid handling solutions. Understanding how chemical pumps function is crucial for optimizing processes.
These pumps are designed to handle aggressive and corrosive liquids safely. They vary in design, including diaphragm, peristaltic, and centrifugal types. Each type has unique advantages and limitations. For instance, diaphragm pumps are excellent for precise dosing, while centrifugal pumps excel in high-flow applications. It’s important to consider the specific requirements of each application.
However, not all chemical pumps meet the industry's stringent standards. Some may suffer from efficiency issues or wear and tear from harsh chemicals. Regular maintenance and assessment are necessary. Companies must learn from past mistakes and strive to improve their chemical pump systems. Investing in high-quality pumps leads to better performance and reduced costs over time.

What are Chemical Pumps? Definition and Overview of Functionality
Chemical pumps are essential devices used to transfer liquids that may be corrosive or hazardous. They are specifically designed to handle harsh chemicals in various industries. The functionality of these pumps is crucial for processes like chemical manufacturing, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals.
A chemical pump typically operates by creating a pressure difference. This process facilitates the movement of liquids from one place to another. The main components include an inlet, outlet, and a mechanism to create flow. Some pumps use centrifugal force, while others rely on positive displacement. This diversity allows them to cater to different applications.
However, not all chemical pumps are perfect. They can fail if the right materials are not used for construction. This can lead to leaks or contamination. Maintenance is vital to ensure they function correctly. Regular checks can prevent unexpected breakdowns. It’s essential to reflect on the prevention strategies to enhance reliability.
Types of Chemical Pumps: Diagrammatic Representation and Applications
Chemical pumps are essential in various industries to manage fluid transport. They handle a range of chemicals, from acids to viscous liquids. Understanding the different types of chemical pumps helps in selecting the right one for specific applications.
Centrifugal pumps use rotational force to move fluids. They are efficient for low-viscosity liquids. Diaphragm pumps employ a flexible diaphragm to create pressure. This makes them ideal for handling corrosive substances. Gear pumps work well for viscous fluids, relying on gears to transfer liquid. Each pump type has its own advantages and is suited for particular tasks, illustrating the diverse needs in chemical handling.
Accuracy in selecting the right pump is crucial. Using an inappropriate pump can lead to leaks or inefficiencies. Maintenance schedules should not be overlooked. Regular checks ensure pumps operate smoothly and safely. Understanding your chemical properties is vital for pump longevity.
What is a Chemical Pump and How Does it Work? - Types of Chemical Pumps: Diagrammatic Representation and Applications
| Type of Pump | Working Principle | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragm Pump | Uses a flexible diaphragm to create pressure differences. | Chemical transfer, food processing, pharmaceuticals. | Good for hazardous liquids, low maintenance. |
| Centrifugal Pump | Utilizes rotational energy to move fluids via centrifugal force. | Water treatment, chemical processing, agriculture. | High flow rates, efficient for low viscosity fluids. |
| Peristaltic Pump | Uses rollers to compress a hose, creating a vacuum effect that moves the fluid. | Medical applications, laboratories, water treatment. | Minimal contamination, accurate dosing. |
| Gear Pump | Utilizes gears to pump fluid by trapping it between gear teeth. | Oil transfer, lubricating applications, hydraulic systems. | Constant flow rate, good for high-pressure applications. |
Key Components of Chemical Pumps: Materials and Design Considerations
Chemical pumps play a crucial role in various industries, handling fluids that can be aggressive or corrosive. The materials chosen for construction significantly impact the pump's performance and durability. Common materials include stainless steel, thermoplastics, and various alloys. Each serves a specific purpose. For example, stainless steel is often favored for its strength and resistance to corrosion.
Design considerations are vital to ensure optimal function. Factors like pressure rating, flow rates, and temperature tolerance must be accounted for. According to recent industry data, improper material selection can result in over 30% of pump failures and lead to significant downtime. Some pumps are designed with modular components for easier maintenance. Such designs reflect a growing trend towards efficiency and sustainability in the chemical industry.
Despite advancements, challenges remain. Many pumps face issues with cavitation and wear. Regular inspection is essential to mitigate these problems. Industry reports indicate that predictive maintenance can reduce operational costs by up to 20%. Thus, understanding materials and design factors is not just useful; it’s necessary for successful chemical pump operation.
Performance Comparison of Chemical Pumps Based on Flow Rate and Material
Operational Mechanics: How Chemical Pumps Move Fluids Effectively
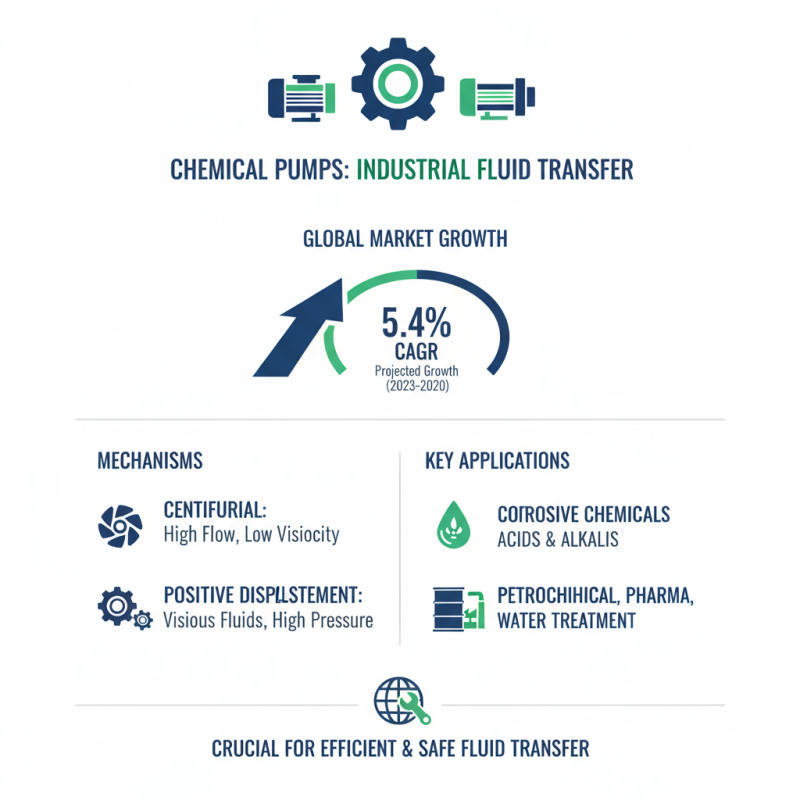
Chemical pumps play a crucial role in various industries by effectively transferring fluids. These pumps utilize mechanisms like centrifugal or positive displacement to ensure the efficient movement of corrosive and viscous materials. According to a recent industry report, the global market for chemical pumps is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4%, underscoring their increasing significance.
Operational mechanics reveal that chemical pumps work by generating pressure differentials. This is achieved through rotating impellers or pistons. They are designed to handle a variety of chemicals with different viscosities. However, their performance can vary under specific conditions. For instance, fluctuating temperatures can affect the viscosity of the fluid, leading to decreased efficiency. Reports suggest that nearly 15% of chemical pump failures are due to improper selection based on fluid properties.
Moreover, maintenance remains a concern. Regular inspections are vital, yet many facilities overlook this necessity. A study highlighted that about 30% of downtime in chemical plants is linked to pump failures. Operators often need to reassess their strategies. By doing so, they can better accommodate the complexities of fluid movement. Identifying and rectifying these issues can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
Industry Standards and Safety Measures in Chemical Pump Usage and Maintenance

When dealing with chemical pumps, safety measures are essential. The pumping of hazardous materials can pose significant risks. Regular maintenance helps in identifying potential leaks or failures. It is crucial to inspect seals and gaskets regularly, as these components are often the first to wear out. Ensuring all fittings are secure can prevent accidents.
Following industry standards reduces the likelihood of mishaps. Proper training for operators is necessary. Many plants lack adequate training programs, leading to safety breaches. Employees must know the correct procedures for handling leaks or spills. Moreover, they should be familiar with emergency shut-off systems. These practices can save lives and property.
Storing chemicals safely is also vital. All chemicals should have appropriate labeling. Incorrect labeling can create confusion and lead to disasters. Regular audits of storage areas can help spot issues. Emergency kits should be easily accessible, but they often collect dust. Reflecting on these factors can help enhance chemical pump safety in various operations.
Related Posts
-
2025 How to Choose the Right Chemical Injection Pumps for Your Needs
-

What is a Chemical Pump? Understanding Types, Uses, and Benefits for Your Industry
-

5 Unmatched Benefits of Using Chemical Metering Pumps for Precision in Industry
-

How to Choose the Right Chemical Diaphragm Pump for Your Application
-

7 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Chemical Injection Pumps
-

Exploring Market Trends for Chemical Feed Pumps at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
