Blog
Best Pump Metering Techniques for Accurate Performance?
In the realm of industrial applications, pump metering plays a critical role in ensuring fluid accuracy and efficiency. According to a recent report from the Fluid Efficiency Association, precise pump metering can enhance operational performance by up to 20%. This statistic highlights the importance of adopting the best techniques in pump metering to achieve optimal outcomes.
Renowned industry expert Dr. Emily Roberts emphasizes, "Accurate pump metering is not just a luxury; it is a necessity for operational excellence." Her perspective sheds light on the urgent need for organizations to refine their approaches in this area. Effective pump metering techniques can prevent costly mistakes and improve overall productivity.
However, the path toward accurate pump metering isn't without challenges. Many organizations still face inconsistencies and errors. Often, outdated methods and equipment are to blame. The industry must reflect on these obstacles to advance in pump metering practices that deliver reliable results. Identifying and implementing cutting-edge methods can help companies overcome these pitfalls and establish a robust framework for pump performance.
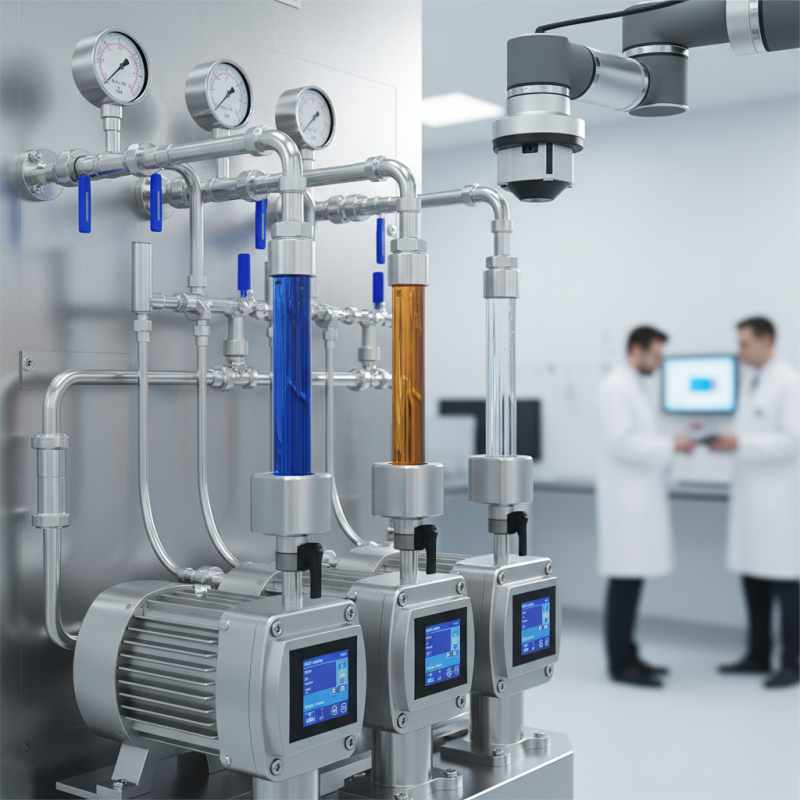

Overview of Pump Metering Techniques
Pump metering is essential for achieving precise fluid delivery in various applications. Different techniques provide varying levels of accuracy and efficiency. One popular method is volumetric metering. This approach measures the volume of fluid displaced by a pump. It’s simple to execute but can be less reliable under varying temperatures or pressures.
Another common technique is mass flow metering. This method uses sensors to measure the mass of the fluid. It offers higher accuracy and can adapt better to changing conditions. However, it may require more complex equipment. In real-world scenarios, users often face challenges in maintaining calibration and ensuring consistent results. Regular monitoring and adjustments are vital to achieving the desired performance.
Smart metering technology is gaining traction. It employs digital sensors and data analytics to enhance precision. This approach offers real-time monitoring, but can introduce new complexities. It requires proper training for operators. As with any technique, the effectiveness of these methods depends on factors like system design and application specifics. Therefore, reflection on each technique's limitations is necessary for continuous improvement.
Importance of Accurate Performance in Pump Metering
Accurate performance in pump metering is critical. It impacts efficiency and operational costs. According to a recent report, 25% of pump-related issues stem from poor metering practices. This statistic highlights how vital precise measurements are for effective operations.
Inaccurate measurements can lead to over-pumping. This can waste resources and inflate energy costs. Data shows that companies lose around $60,000 annually due to inefficient pumping systems. A small error in metering can snowball into significant losses over time. Regular calibration and maintenance of pump meters are essential to prevent such issues.
Additionally, improper performance affects product quality. Industries relying on exact fluid measurements risk compromising their final product. A recent survey indicated that 40% of respondents reported quality control issues tied to inaccurate meter readings. Continuous training of staff on best practices also plays a role. Frequent training can enhance awareness and minimize errors. Inaccurate performance is an ongoing concern. It requires diligence and commitment from all stakeholders to ensure accuracy in pump metering.
Common Methods for Pump Metering Accuracy
Accurate pump metering is crucial in many industries. Different techniques ensure precise measurements. Common methods include
volumetric metering,
mass flow metering, and
pressure differential measures. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses.
Volumetric metering uses the volume of fluid to gauge flow. It is simple and reliable, but can lack precision at low flow rates.
Meanwhile, mass flow metering offers high accuracy. It measures the mass directly, which can be beneficial in varying densities.
Yet, it often requires more complex setups and maintenance.
Tips:
Regularly calibrate your meters to maintain accuracy. A schedule can prevent drift over time. Employ a range of techniques for cross-verification. This approach helps identify discrepancies.
Pressure differential methods provide insights into flow rates. They rely on pressure changes across a constriction. While useful, they can be affected by viscosity and temperature variations. Not every system will function well with this method, so assess your needs.
In measuring pump performance, remember, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Each method has limitations. Evaluating them can lead to better choices and enhanced accuracy. Consistency in measurements is key.
Factors Influencing Pump Metering Performance
When it comes to pump metering performance, several factors play a critical role. The fluid properties, like viscosity and temperature, can affect accuracy. For instance, high-viscosity fluids require careful handling to ensure proper flow rates. Temperature changes may alter fluid density, impacting measurement. It's essential to monitor these variations closely.
**Tip:** Regular calibration can help mitigate discrepancies in readings. This process ensures that meters reflect true performance.
Another important consideration is pump design. The type of pump selected may influence metering accuracy. Positive displacement pumps often provide better precision compared to centrifugal types. However, their maintenance can be more complex. Ensure you understand the implications of your choice.
**Tip:** Evaluate your operational needs before selecting a pump. This helps align your equipment with performance expectations.
Environment also matters. External factors, such as vibration and pressure fluctuations, can interfere with metering. Pumps installed in less-than-ideal conditions may yield inconsistent results. Regular checks in different scenarios can provide insight into performance limits.
**Tip:** Keep the installation area clean and organized. A tidy environment contributes to consistent pump operation.
Best Pump Metering Techniques for Accurate Performance
| Technique | Accuracy (%) | Factors Influencing Accuracy | Operational Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volumetric Metering | 95 | Fluid viscosity, temperature | 200 |
| Mass Metering | 98 | Temperature, pressure fluctuations | 250 |
| Ultrasonic Metering | 97 | Flow profile, aeration | 300 |
| Electromagnetic Metering | 96 | Conductivity, temperature | 220 |
| Diaphragm Metering | 94 | Pressure, pump performance | 180 |
Implementing Best Practices for Enhanced Metering Accuracy
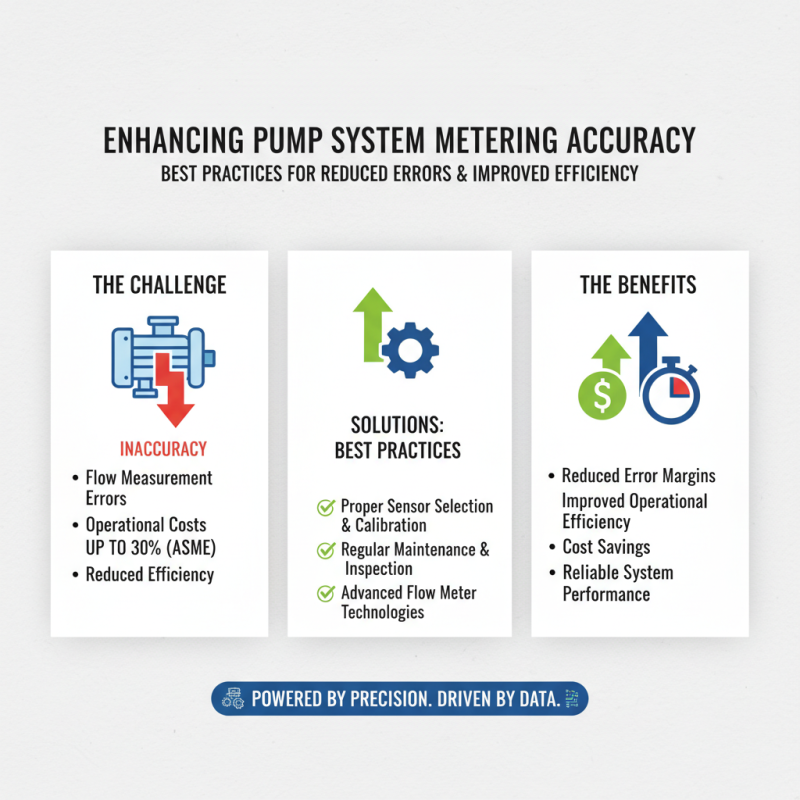
To enhance metering accuracy in pump systems, best practices must be implemented. This can significantly reduce error margins and improve operational efficiency. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, inaccuracies in flow measurement can lead to operational costs rising by up to 30%. This emphasizes the need for robust metering techniques.
Regular calibration is crucial. Many operators neglect this aspect, assuming that their systems are always accurate. However, studies show that up to 15% of flow meters can drift out of calibration over time. Monitoring the condition of these meters ensures they perform optimally and reduces unexpected downtime.
Additionally, training personnel on best practices is essential. Many accidents arise from improper handling or misunderstanding of equipment functionalities. A survey conducted by the International Society for Measurement and Control highlights that 25% of metering failures stem from human error. Enhancing training programs can mitigate these risks, resulting in more precise measurements. Implementing these strategies can transform metering processes and lead to more accurate performance metrics.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Pump Systems for Your Specific Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Tank Mixer for Your Industrial Needs
-

2025 Top Metering Pump Innovations for Precision Fluid Control
-

Essential Tips for Choosing a Chemical Metering Pump System?
-

How to Choose the Right Commercial Pump for Your Business Needs
-
Understanding the Mechanics of Diaphragm Pumps: The Key to Efficient Fluid Transfer
